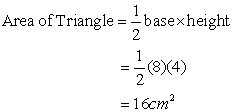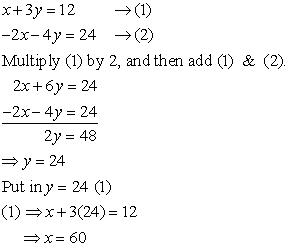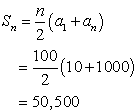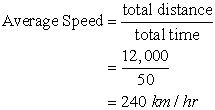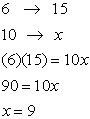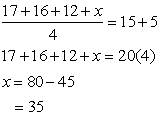The Analytical Reasoning section of GAT General is consist of the questions like, Deductive and inductive logic, Critical thinking and writing skills. In other words, there will be some statements bearing some information and you need to deduce and infer other relevant information. Find sample questions of the Analytical section of the NTS Test here. Also, find answers and explanation to the answers at the bottom of the page.
NTS ANALYTICAL REASONING SECTION: SAMPLE QUESTIONS
Find answers and explanation to the answers at the bottom of the page.
Questions 1 – 7
Nine individuals: Ahmed, Bilal, Danish, Faisal, Haroon, Liaquat, Maryam, Shiza and Zeeshan are to serve on three committees labeled A, B and C.
- Each candidate should serve on exactly one of the committees
- Every committee must have atleast one member
- Committee A should consist of exactly one member more than that of committee B
- Among Maryam, Shiza and Zeeshan none can serve on committee A
- Among Faisal, Harron and Liaquat none can serve on committee B
- Among Ahmed, Bilal and Danish none can serve on committee C
QUESTIONS
1. In case Danish and Zeeshan are the individuals serving on committee B, how many of the nine individuals should serve on committee C?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
(E) 6
2. Of the nine individuals, the maximum number that can serve together on committee C is
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 7
(D) 8
(E) 9
3. In case Ahmed is the only individual serving on committee B, which among the following should serve on committee A?
(A) Bilal and Danish
(B) Bilal and Faisal
(C) Bilal and Liaquat
(D) Faisal and Haroon
(E) Danish and Haroon
4. In case, any of the nine individuals serves on committee C, which among the following could not be the candidate to serve on committee A?
(A) Ahmed
(B) Bilal
(C) Danish
(D) Liaquat
(E) Shiza
5. In case, Bilal, Danish and Maryam are the only individuals serving on committee B, the total membership of committee C should be
(A) 5
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 2
(E) 1
6. In case, Bilal, Danish and Maryam are the only individuals serving on committee B, then the members of committee C should be
(A) Haroon and Shiza
(B) Maryam and Zeeshan
(C) Shiza and Zeeshan
(D) Faisal and Shiza
(E) Haroon and Maryam
7. Among the following combinations which could constitute the membership of committee C?
(A) Danish and Shiza
(B) Faisal and Maryam
(C) Liaquat, Maryam and Shiza
(D) Faisal, Haroon and Liaquat
(E) Ahmed, Faisal, Maryam and Zeeshan
ANSWERS
1(C) 2(B) 3(A) 4(E) 5(D) 6(C) 7(B)
EXPLANATION
1. (C) If Danish and Zeeshan (two persons) are in committee B, then there must be 3 persons in committee A. Hence, 4 persons should serve in committee C.
2. (B) If minimum 1 in committee B, then committee A must have 2 members. Hence, committee C could have maximum of 6 members.
3. (A) If Ahmed is the only (one person) serving in committee B. Then committee A must have 2 members. And, committee C cannot have Ahmed, Bilal and Danish. Hence, Bilal and Danish should serve in committee A.
4. (E) Committee A cannot have Maryam, Shiza and Zeeshan. Hence, Shiza cannot serve in committee A.
5. (D) If 3 members in committee B then 4 members in committee A. Hence, 2 members in committee C.
6. (C) If Bilal, Danish and Maryam (3 persons) are serving in committee B. Then, committee A must have 4 persons and cannot have Maryam, Shiza and Zeeshan. Hence, Shiza and Zeeshan should be in committee C.
7. (B) If committee B=1, A=2 then C=6. If committee B=2, A=3 then C=4. If committee B=3, A=4 then C=2. So, committee C cannot have odd number of members. And, committee C cannot have Ahmed, Bilal and Danish. Hence, it should have Faisal and Maryam.
 and y in the following pair of equations
and y in the following pair of equations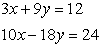 (A)
(A) 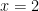 and
and 
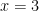 and
and 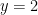
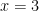 and
and 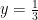
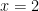 and
and 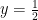
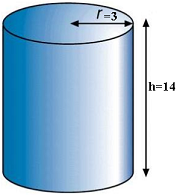 (A) 384 cm3
(A) 384 cm3 (A) 384 cm3
(A) 384 cm3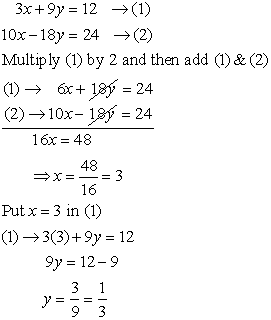
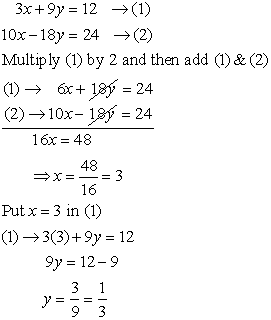
 . Thus,
. Thus,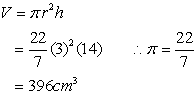
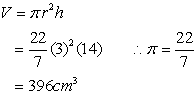
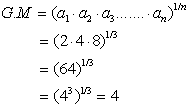
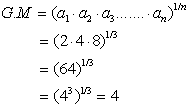
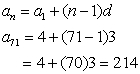
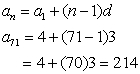




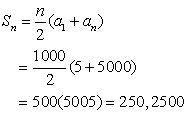 NOTE: There are 1000 terms from 5 to 5000, so n = 1000.
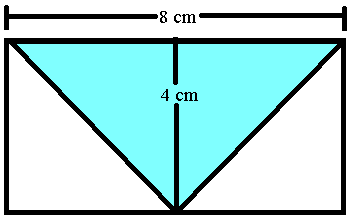
NOTE: There are 1000 terms from 5 to 5000, so n = 1000.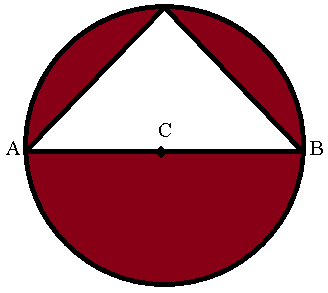 What is the area of the shaded region (region in maroon colour)?
What is the area of the shaded region (region in maroon colour)?
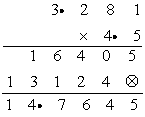 3.281 ⇒ three digits after decimal
3.281 ⇒ three digits after decimal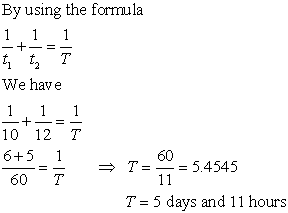
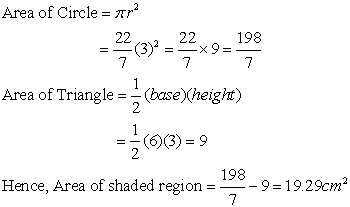
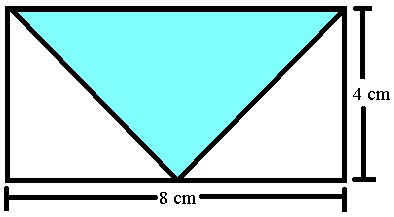 (A) 16 cm2
(A) 16 cm2